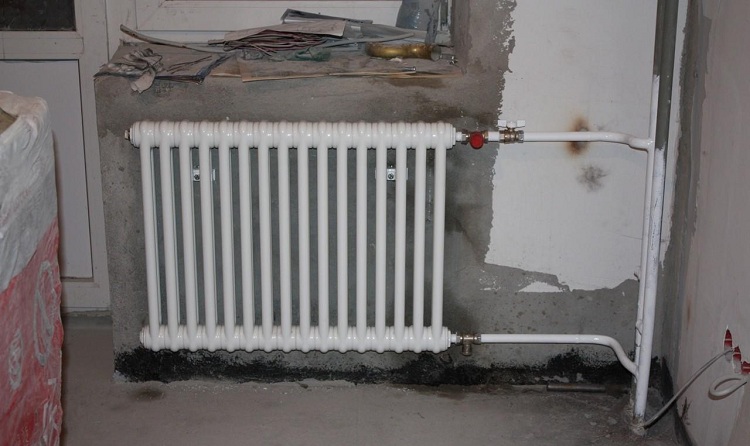
An important criterion when choosing a heating radiator is the combination of functionality with visual design. You can often see batteries and pipes wired with drywall or wooden screens, the reason for this is that they do not fit into the interior. The most ordinary-looking are cast-iron radiators. Although they have good performance, no one prefers them. The construction and design industry today offers a wide selection of heating appliances in which aesthetics and functionality are balanced. These include pipe radiators.

Due to the aesthetic appearance, tubular heating radiators are often used as an addition to the interior.
Content
Features of tubular devices
Tubular heating radiators - non-separable metal construction, consisting of interconnected pipe steel sections, less often aluminum, copper or stainless steel. The diameter of the tubular elements is 25 mm (the type of section is not limited), the wall thickness is 1 - 2 mm. The configuration of such equipment can be varied, made to individual sketches to order. Height varies from 20 cm to 3 m, length from 27 cm to 3 m, depth from 32 mm to 300 mm. One section holds from 2 to 6 pipes. You can select the number of sections and the plane of their location (horizontal, vertical). The connection is rectilinear or complex in shape by laser welding, so that the seam is hardly noticeable. The location is wall, floor (installation on legs), a room partition, a bench. These batteries are suitable for centralized and autonomous heating systems.
Inside the radiator, the working medium circulates through the channels (coolant, water), which is supplied heated to a certain temperature. Steel pipes, warming up quickly, begin to quickly give off heat to the space of the room. Heat transfer increases with the increase in the number of pipes in one section, its size.
For autonomous systems, convector tubular radiators are gaining popularity. Each pipe is enclosed in a round case. While a heat carrier of high temperature is supplied to the radiator, the cover protects a person from tactile contact with a hot surface and provides effective circulation of air masses due to the space between the pipe and the cover. The flow of hot air rushes up and the room warms up thanks to powerful heat transfer. The device is equipped with a temperature controller.
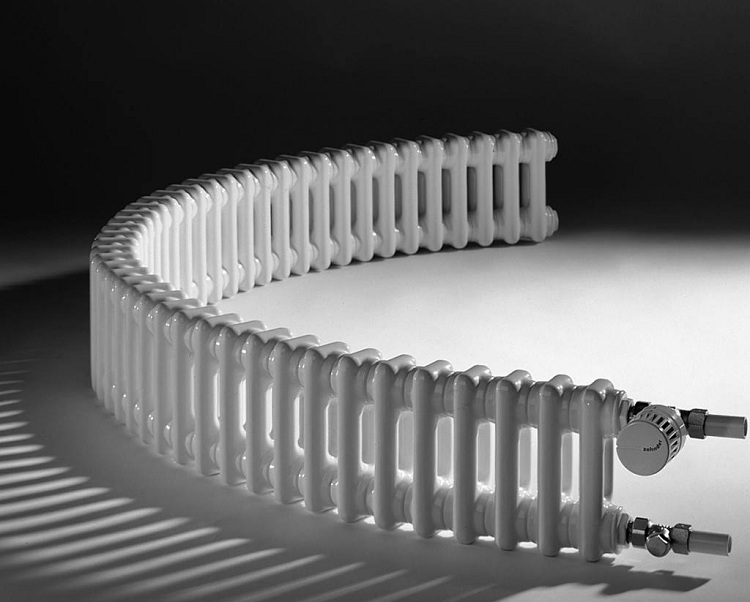
Tubular type devices are equipped with temperature controllers that allow you to control the temperature in the room
The enterprises engaged in the production of domestic tubular radiators adapted them to the local operating conditions. This is the heterogeneity and aggressive properties of the coolant, its high temperature in the northern latitudes, and the irregular pressure in the system. By increasing the wall thickness to 2 mm, it was possible to increase the working pressure to 22 atm, to make the batteries more resistant to wear.
Product Features
Functional parameters of steel tubular radiator:
- medium temperature 110aboutC - 130aboutWITH;
- operating pressure 10 - 22 atm (depending on material, manufacturer and configuration);
- corrosion resistance (polymerization of internal surfaces, wall thickness 1.5-2mm);
- hygienic surface (an additional antibacterial layer is applied);
- light weight;
- service life of 10-25 years.
Advantages of steel tubular radiator:
- a wide selection of structural forms, the possibility of individual selection of configurations and external coating (painting, varnishing, structural coating, galvanizing);
- low inertia, good heat dissipation, uniform heating of the room;
- reliable welded joint;
- smooth inner and outer surface;
- ease of care (does not require frequent dust removal due to design features);
- shape safety, lack of sharp corners;
- the ability to fit into any interior, save space;
- many connection schemes.
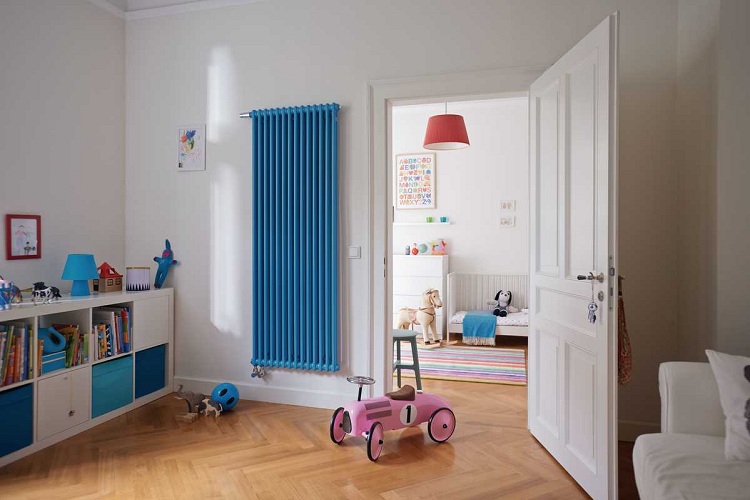

Radiators are characterized by a high degree of safety and do not require the installation of protective screens even in children's rooms
Disadvantages of a steel tubular radiator:
- high price;
- not resistant to pressure drops in a centralized system;
- spot welding is not reliable with frequent water hammer;
- thin-walled pipes (1 mm) without additional coatings are susceptible to corrosion and abrasion due to the aggressive medium of the coolant (impurities, solid particles).
Important! For apartment buildings with a centralized heating system, a device made of high-quality steel should be selected with the following parameters: working pressure not lower than 13-15 atm, coolant temperature not lower than 120aboutWITH.
Often, shortcomings are manifested in connection with improper or poor-quality installation (leaks, corrosion), incorrect choice (low heat transfer). In order not to make a mistake and choose the right tubular heater, you should take into account the nuances.
How to choose steel tubular heating radiators
In order for the device to be powerful enough and warm the entire volume of the room, it is necessary:
- determine the area of the room, the height of the ceiling;
- calculate the amount of heat transfer for a given room. Premises (with window and door) with an area of 10 m2 1000 watts is enough. In the technical characteristics of the radiator, the manufacturer indicates the heat transfer of one section (2-6 tubular) or the whole structure. The more tubes in the section, the more efficient the heating of the room, one minus - the design looks bulky. So, for example, a two-row section of 560 mm high and 90 mm deep has a heat transfer of 160 W;
- according to calculations, select such a number of sections so that there is enough power;
- additional sections need to be added if the room is cold, angular, on the north side;
- 4% should be added to the calculated heat transfer if the ceiling height is more than 3 m;
- placing the radiator in a niche or under a drywall panel with slots reduces the heating of the room by 5-15%;
- Selecting a dark colored battery increases heat emission.
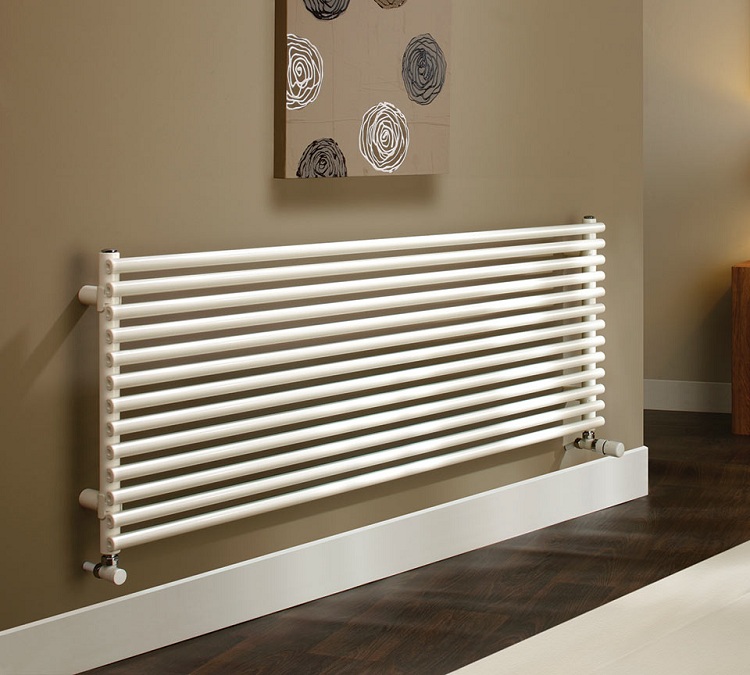

The shape, size and number of sections of the radiator can be any, depending on the area of the room and personal wishes
Connecting a steel tubular radiator
There are many connection schemes, it can be two-pipe or single-pipe, with lateral, upper, lower pipe connections. Once the location for the installation of the radiator is determined, it is fixed using brackets (depending on the model), and then piping and connection are started.
Important! For any design for mounting and connecting a heating device, direct access to the docking points, valves should be provided.
The choice of connection option also helps the aesthetic organization of space. It is possible to lay the pipeline covertly under the floor or in the wall and bring it directly to the radiator pipe. Mounting the radiator is available easily for independent execution. The accompanying instruction contains the procedure, diagrams and installation tips.
The lower (upper) connection option is used when choosing a radiator of large length. Possible schemes:
- two-pipe bottom, top, side by side (feed / return pipelines near left or right), central (supply / return pipelines are lower in the center, if the sections are even, if odd, then shift to one side);
- single-tube bottom for valve with injection tube (Ø11 mm, length 150 mm, return pipe).
The lateral connection option is most often used for a small number of sections and high radiators. Possible schemes:
- two-pipe lateral left, right (supply / return pipelines are connected on the one hand to the upper and lower nozzles), diagonal (flow on the upper right, return on the lower left or vice versa);
- one-pipe lateral for the valve with an injection tube (Ø11 mm, length 70 mm, return pipe).
Tubular radiator in the interior
Steel tubular heating radiators look spectacular, therefore organic for any interior. They combine both with antiques and hi-tech design. The whole secret is the simplicity of the design, from which a variety of forms is created, a wide color palette and the choice of a convenient location.
In addition to the classic arrangement of the device on the wall under the window opening, the tubular radiator can be used as a bench, wall partition, legs for countertops, railings, framing the mirror on the wall, columns of the false fireplace. Such a radiator is equally aesthetic and functional in any space: a hall, a kitchen, a bathtub, a nursery, an exhibition hall, a cafe, institutions with increased sanitary and hygienic requirements, etc. The need to hide the batteries disappeared, they became a tool in creating a unique interior design.
The steel tubular radiator is distinguished by a host of positive qualities, is technically efficient, safe, and most importantly takes its rightful place in the room, endowing it with personality and warmth.






