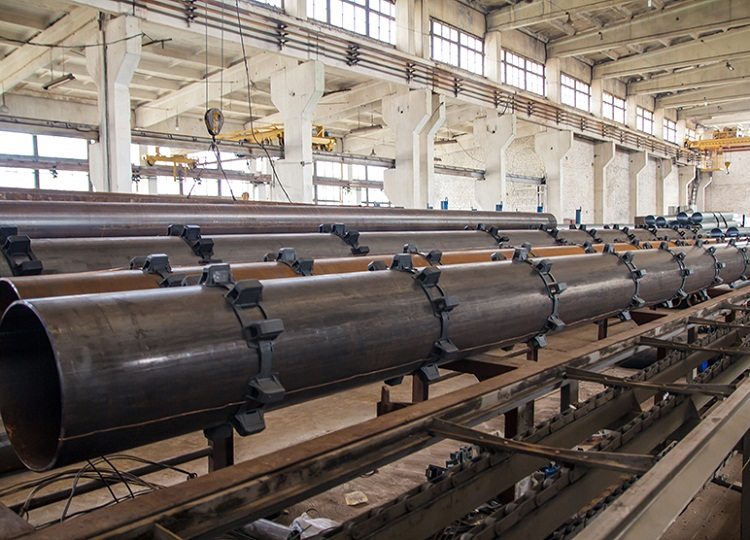
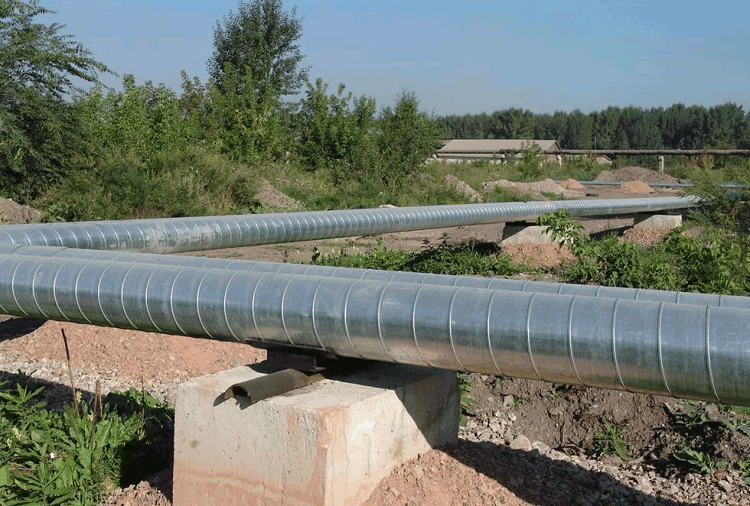
Pipes designed for water supply or heating require high-quality thermal insulation, especially when it comes to external systems. Insulation helps to reduce heat loss and costs aimed at heating the coolant. Also, the insulating shell prevents the rapid wear of the pipeline, protects it from mechanical damage and the appearance of corrosive formations.
Content
What are galvanized insulation pipes?
A pipe in an insulating shell is the following construction: one pipe, usually made of simple "black" steel, is wrapped with a layer of insulation, and then placed in a shell of a larger diameter. Polyurethane foam (PPU-sheath) is used as insulation, and the outer steel pipe is coated with a galvanized layer. There are also products in which the outer shell is represented by polyethylene: then in the lettering of the PPU pipe there will be a PE marking, and not OC.
ATit is important! For structures in a PE shell, there are 2 categories: the first category (1 type) denotes the standard pipe configuration, the second (2 type) - reinforced.
PUF is a type of plastic. The properties of polyurethane foam insulation surpass all other types of insulation (mineral or basalt cotton wool, other polymeric materials) in all respects. The wear resistance of polyurethane foam is much higher than that of other polymers. Among all insulating materials, polyurethane foam is the least heat-conducting material.
In addition to insulation, PPU pipes have an additional built-in cable, which enables remote monitoring and timely diagnosis of problem sections of the pipeline. Remote control is a successful development to optimize service and increase the operational life of large heating and water networks.
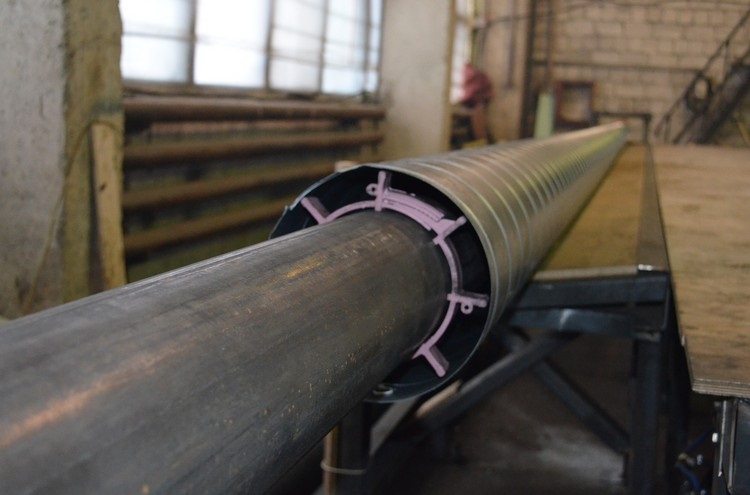

For the manufacture of a tubular product PPU OTs, one pipe is inserted inside another, and then the gap between them is then filled with polyurethane foam
Conductors are parallel to the passage of the axis of the product. They pass through the centering support devices at an optimum distance of 20 mm from the surface of the galvanized pipe. The cable must pass with tension. The electrical resistance between the inner pipe and the conductor (as well as between the outer galvanized shell and the conductor) must be at least 100 MΩ.
Characteristics of PPU galvanized and PE pipes
Technical characteristics of galvanized heat-insulated pipes and fittings for it must comply with the requirements presented in this table.
Table 1
| Galvanized pipe property | Characteristic |
| The density of the middle insulating layer | No less 60 kg / m3 |
| Water absorption when in boiling water in flow. 90 min | 10% of the total |
| Strength at 10% deformation by radial compression | No less 0.3 MPa |
| Thermal conductivity at a temperature of +50 degrees (average working) | No more 0,033 |
| Index for PE pipes: shear strength in the direction: along the axis, at temperature 23 +/- 2 degrees 140 +/- 2 degrees |
0.12 MPa 0.08 MPa |
| Shear strength in the direction: tangential, at temperature 23 +/- 2 degrees 140 +/- 2 degrees |
0.2 MPa 0.13 MPa |
| The radial creep rate of the insulating layer at a test temperature of +140, during 100 h 1000 h |
2.5 mm 4.6 mm |
Both OTs and PE PPU pipes possess the increased moisture resistance. The ends of the polyurethane foam insulation may also have a waterproofing coating. Welds of steel products undergo a mandatory leak test.
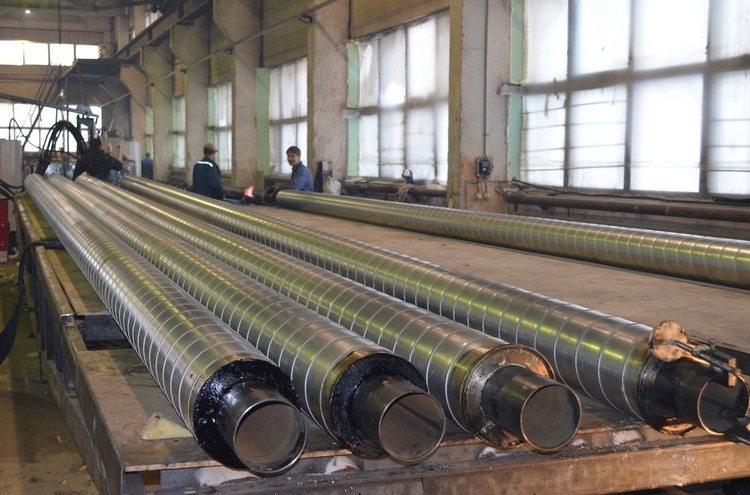

The ends of the PPU pipes can have a protective coating that prevents moisture from entering the structure
The design of the galvanized PU foam pipe assumes that from the two ends of the product, the inner steel part must remain open, without insulating material. The length of the free edge segment should be 150 mm for the inner diameter with a value from DN 25 to DN 219 and 210 mm for DN 273-DN 1020.
External polyethylene shells have the characteristics presented in table 2.
table 2
| Polyethylene Shell Property | Feature Description |
| Nominal elongation at break | Not less than 350% |
| Elongation of the shell surface during heating by +110 degrees | No more than 3% |
| Resistance to a working load of tensile 4 MPa in an aqueous solution of a surfactant (at a temperature of +80 degrees) | 2000 |
| Resistance to working pressure and temperature +80 degrees | 165 - at a wall voltage of 4.6 MPa
1000 - at a wall voltage of 4 MPa |
The visual requirements of pipes are such requirements:
- The surface is smooth.
- Allowed: unexpressed longitudinal strips and waves that do not increase the pipe walls beyond the limits of deviations.
- Not allowed: burrs at pipe ends, bubbles, cracks, inclusions of foreign materials on the inner and outer surfaces.
Requirements for PPU pipes in galvanized shell
The durability and uninterrupted operation of the pipeline depend on the quality of the materials used in the production. The standards for the production of products in galvanized and PE insulation are regulated by GOST 30732-2006. The basic requirements for the plants will be as follows:
1. For insulation, it is permissible to use solid polyurethane foam that meets the industrial standards of GOST. Between the surface of the inner pipe made of black steel and insulating foam, the adhesion should be as tight as possible (full adhesion is guaranteed). The degree of adhesion is evaluated in tests for shear of the material along the axis: the axial shift is not more than 0.14 MPa at a temperature of +23 degrees.
2. Pipes are made from carbon or low alloy steel grades of the highest quality. The best option for manufacturing is a straight-line or seamless method.
Important! The internal structure is subject to bead-blasting and visual inspection before applying the protective coating.
3. For pipes in PE sheath, only black polyethylene is allowed. Polymers of the brand PE 80 or PE 100 are used, manufactured in accordance with GOST 18599-2001. Pipes with a polyethylene sheath are also checked according to the indicators set forth in the standard under the number 30732-2006, and if they do not comply, they are not allowed for sale.
4. For external protection, the PPU OTs pipe is coated with sheet steel with a wall thickness not exceeding 1 cm. Class 1 galvanizing is applied to it (GOST 52246-2004). OTs coating should be applied in conditions of complete tightness.
5. Polyurethane foam in the end section of the product with insulation should have a uniform, fine-grained texture. If there are voids in the insulation layer, the size of which exceeds 1/3 of the total thickness of the foam, such a product should be rejected.
Pipe sizes in PE and OC shell
The standard sizes of pipes with insulation in polyethylene are presented in table 3.
Table 3
| External d and minimum permissible steel pipe wall thickness | Type 1 | Type 2 | ||||
| Rated outside d | The thickness of the PUF layer | Rated outside d | The thickness of the PUF layer | |||
| Marginal deviation
|
Estimated | Marginal deviation
|
Estimated
|
|||
| 32; 3 | 2,7 — 3,7 | 90 – 125 | 26 – 43,5 | – | – | – |
| 38; 3 | 3,2 — 3,7 | 110 – 125 | 33 – 40,5 | – | – | – |
| 45; 3 | 3,7 | 125 | 37 | –– | –– | –– |
| 57; 3 | 3,7 | 125 | 31 | 4,1 | 140 | 38 |
| 76; 3 | 4,1 | 140 | 29 | 4,7 | 160 | 39 |
| 89; 4 | 4,7 | 160 | 32,5 | 5,4 | 180 | 4,25 |
| 108; 4 | 5,4 | 180 | 33 | 7,4 | 200 | 43 |
| 159; 4 | 7,4 | 225 | 41 | 8,3 | 280 | 54,5 |
| 219; 4 | 9,8 | 250 | 42 | 10,4 | 355 | 55,5 |
| 273; 7 | 11,7 | 319 | 57 | 13,2 | 450 | 62 |
| 325; 7 | 13,2 | 400 | 55,5 | 14,6 | 500 | 81,5 |
| 426; 7 | 16,3 | 560 | 58,2 | 16,3 | 600 – 630 | 79,5 |
| 530; 7 | 20,4 | 710 | 72,6 | – | – | – |
| 720; 8 | 26,3 | 900 | 76 | – | – | – |
| 820; 9 | 29,2 | 1000 | 72,4 | 32,1 | 1100 | 122,5 |
| 920; 10 | 32,1 | 1100 | 74,4 | 35,1 | 1200 | 120,5 |
| 1220; 11 | 35,1 | 1425 | 79 | – | –– | – |
| 1420; 12 | 41,2 | 1600 | 90 | –– | –– | –– |
To study the standard sizes of pipes in a galvanized steel sheath, see table 4.
Table 4
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Conductors are made of uninsulated flexible copper MM. The cross section of the indicators is 1.5 mm2. With a diameter of 530 mm, three control cables are installed on the structure.
Pipes with insulation with a diameter of up to 426 mm (inclusive) are equipped with two indicator wires.
Helpful advice! The insulation efficiency is determined by the thickness of the layer. Depending on this, the insulating layers are divided into two types: 1 PUF (for areas located in the temperate climatic zone) and 2 PUF (for areas with cold winters).
The thickness of the insulating layer may vary depending on the individual wishes of the customer. In this case, the wall thicknesses of the inner pipe and the shell should remain the same.
Laying structures with insulating material is carried out in the following ways:
- overhead laying method;
- channelless method, when laying in the ground without digging a trench;
- with the use of sliding supports in tunnels or channels;
- during reconstruction of existing heating systems, laying of a sand “half” in places with impassable canals is used.
The use of pipes in the insulation of PPU OTs
Pipes appeared in mass sales abroad in the seventies of the last century, and relatively recently in the territory of the present CIS. Foreign experience of using suggests that these designs can be completely safely used in most industries and global energy supply.
The main area of application of these products was the construction of pipelines for heat mains. Pipes with PU foam insulation in galvanized or PE sheaths are often used as a replacement for spent heat pipes with increased accident rate. Replacing old heating routes with new insulated pipes is a more economical measure than the constant maintenance and repair of failed structures.
Also, insulated products are successfully used for laying cold and warm water supply networks, gas pipelines and oil pipelines.
Advantages and disadvantages of products with polyurethane foam insulation
Like any metal products, pipes in polyurethane foam coated with a galvanized shell have both advantages and significant disadvantages.
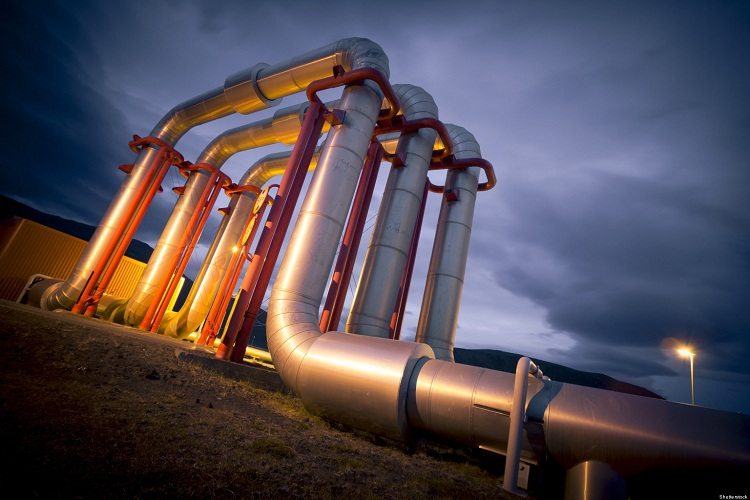

Such pipes are successfully used not only for the installation of heating mains, but also for the construction of oil and gas pipelines
The advantages of PPU products will be as follows:
- Low coefficient of thermal conductivity (heat loss does not exceed 1-2%), high density of the material.
- A wide range of operating temperatures: from -170 degrees to +130 degrees.
- The operational life of the design, subject to constant monitoring, is from 25 to 35 years.
- As a rule, products are equipped with the necessary parts for installation: bends, tees, expansion joints and fittings.
- Compared to other insulated structures (PPM or APB), the weight of the PPU pipelines will be the smallest.
- Convenient monitoring system, cost savings on manual verification and system maintenance.
- Thermal insulation is safe for the environment. With the right pattern of use, the polymer does not release toxic substances into the soil and does not have a detrimental effect on the human body.
Cons of PPU pipes:
- The foam insulation layer is highly flammable. Therefore, the effects of open flame on the end sections of the polymer are not allowed.
- Polyurethane foam, despite its durability, is not resistant against mechanical damage.
- Black steel in any case remains susceptible to corrosion. In the event of insulation leakage, this process occurs quickly and imperceptibly.
- There are restrictions on the use of these products in high-temperature heating networks operating with temperatures from +140 degrees to +170 degrees.
- Careful monitoring of the humidity of the insulating layer is required. When the insulation gets wet, it is necessary to replace a full section of the heating system: PPU cannot be replaced separately.
PPU pipelines in galvanized or polyethylene sheath are modern, cost-effective designs. With proper installation and operating conditions, emergency situations in systems occur extremely rarely, and heat losses during transportation of media are negligible.